3.1. Sequences
Example 3.1.3(c):
{ n / 2n } = { 0, 1/2, 1/2, 3/8, 1/4, 5/32, ...}. It is not clear, but it seems as if the terms get smaller and smaller. Indeed this is the case, and we will prove it:
First, we can use induction to show that
n2for n > 3. But then we have that2n
n2 / 2nor equivalently1
n / 2nfor n > 3. But now you should be able to finish the proof yourself. As a hint, for a given1/n
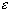 , choose
, choose
N = max{3, 1/}
 Interactive Real Analysis
Interactive Real Analysis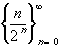 converges to zero.
converges to zero.